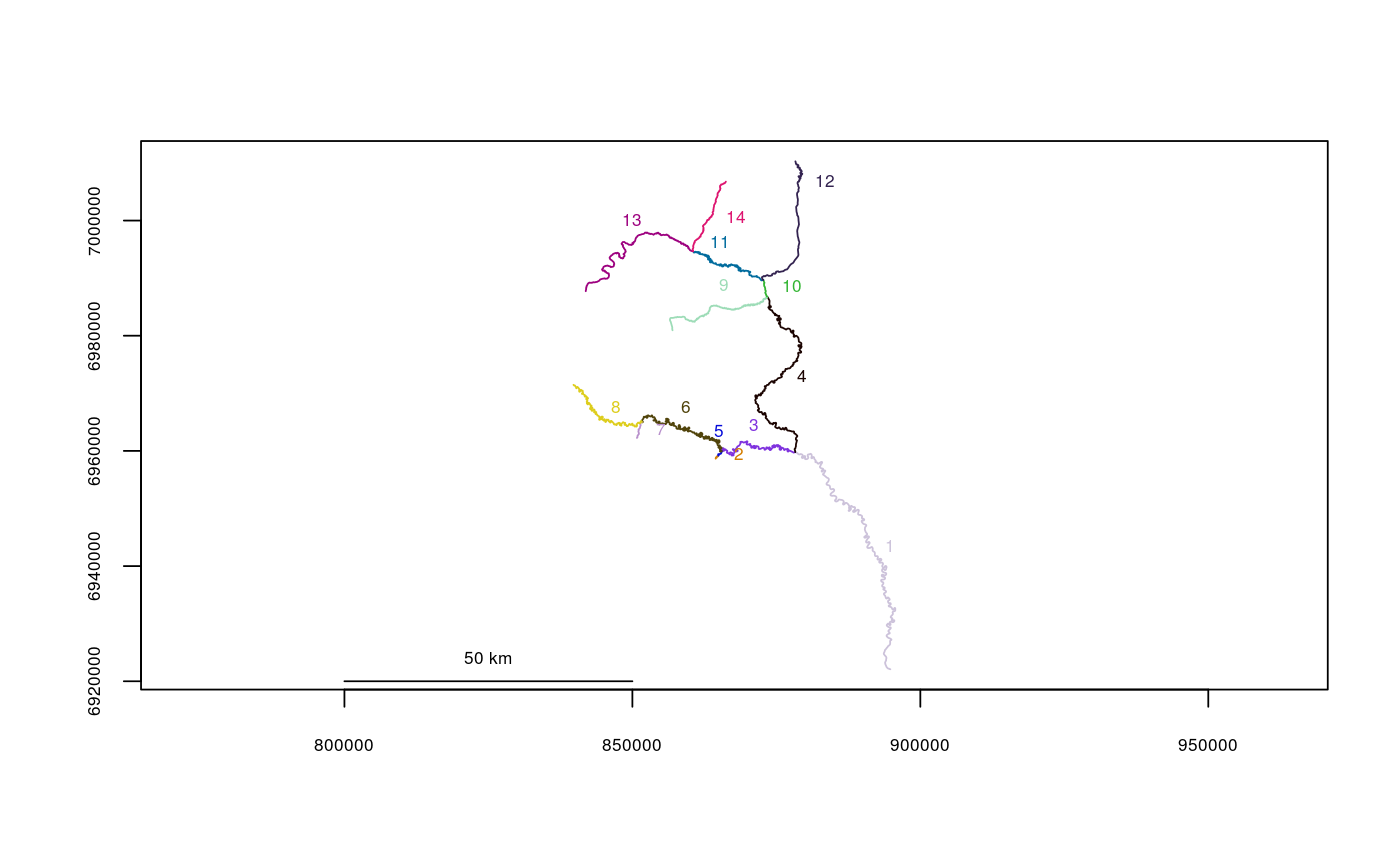
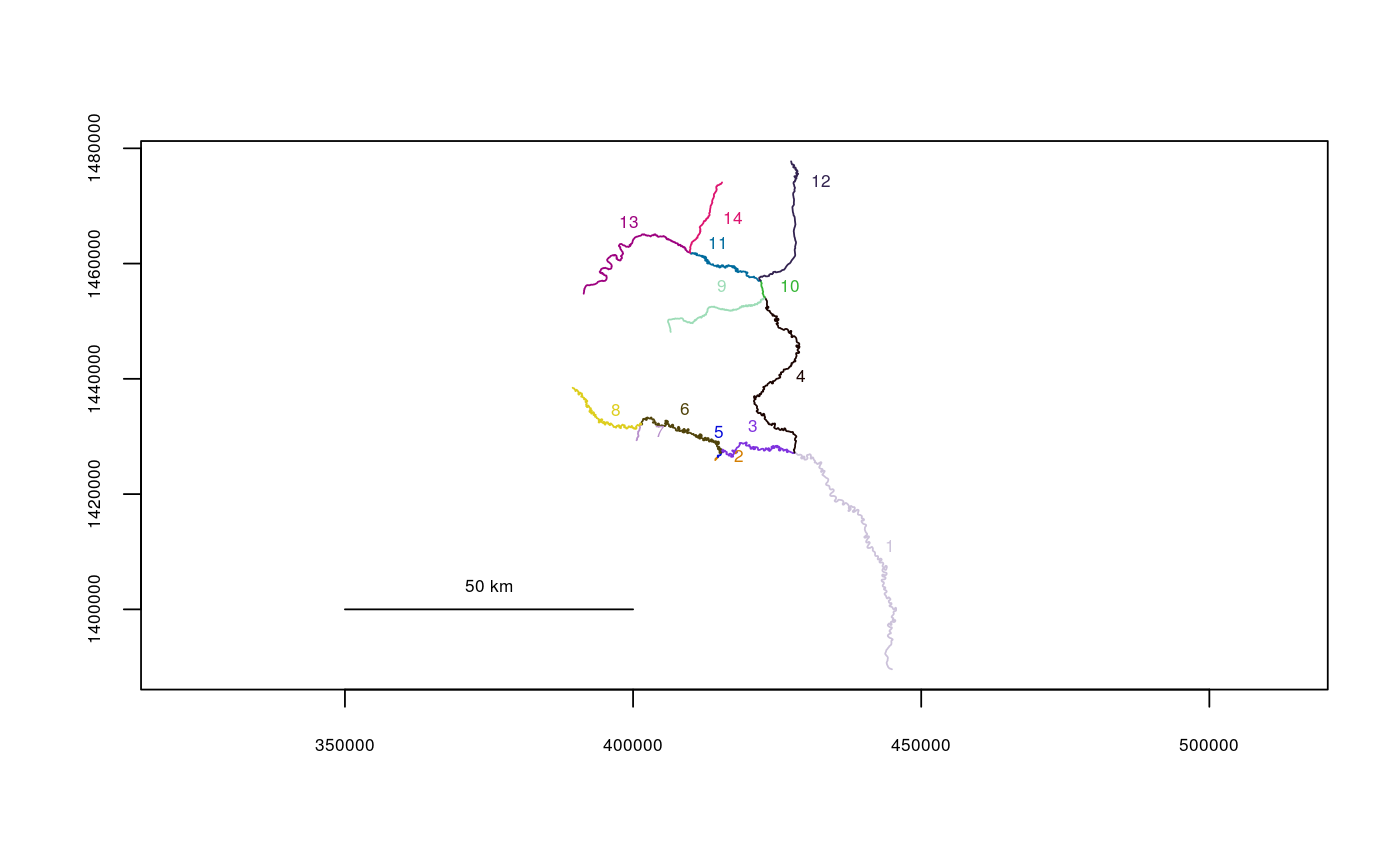
Create a River Network Object from a Shapefile
Uses readOGR in package 'rgdal' to read a river shapefile, and establishes connectivity of segment endpoints based on spatial proximity.
line2network(path = ".", layer, tolerance = 100, reproject = NULL, supplyprojection = NULL)
Arguments
| path | File path, default is the current working directory. |
|---|---|
| layer | Name of the shapefile, without the .shp extension. |
| tolerance | Snapping tolerance of segment endpoints to determine connectivity. Default is 100, therefore care should be exercised when working with larger units of distance, such as km. |
| reproject | A valid Proj.4 projection string, if the shapefile is to be re-projected. Re-projection is done using spTransform in package 'sp'. |
| supplyprojection | A valid Proj.4 projection string, if the input shapefile does not have the projection information attached. |
Value
Returns an object of class "rivernetwork" containing all
spatial and topological information. See rivernetwork-class.
Note
Since distance can only be calculated using projected coordinates,
line2network() will generate an error if a non-projected input
shapefile is detected. To resolve this, the shapefile can be re-projected
in a GIS environment, or using reproject=, shown in the second
example below.
Examples
filepath <- system.file("extdata", package="riverdist") Gulk_UTM5 <- line2network(path=filepath, layer="Gulk_UTM5")#> #> Units: mplot(Gulk_UTM5)# # Re-projecting in Alaska Albers Equal Area projection: AKalbers <- "+proj=aea +lat_1=55 +lat_2=65 +lat_0=50 +lon_0=-154 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +datum=NAD83 +units=m +no_defs +ellps=GRS80 +towgs84=0,0,0" Gulk_AKalbers <- line2network(path=filepath, layer="Gulk_UTM5", reproject=AKalbers)#> #> Units: mplot(Gulk_AKalbers)